
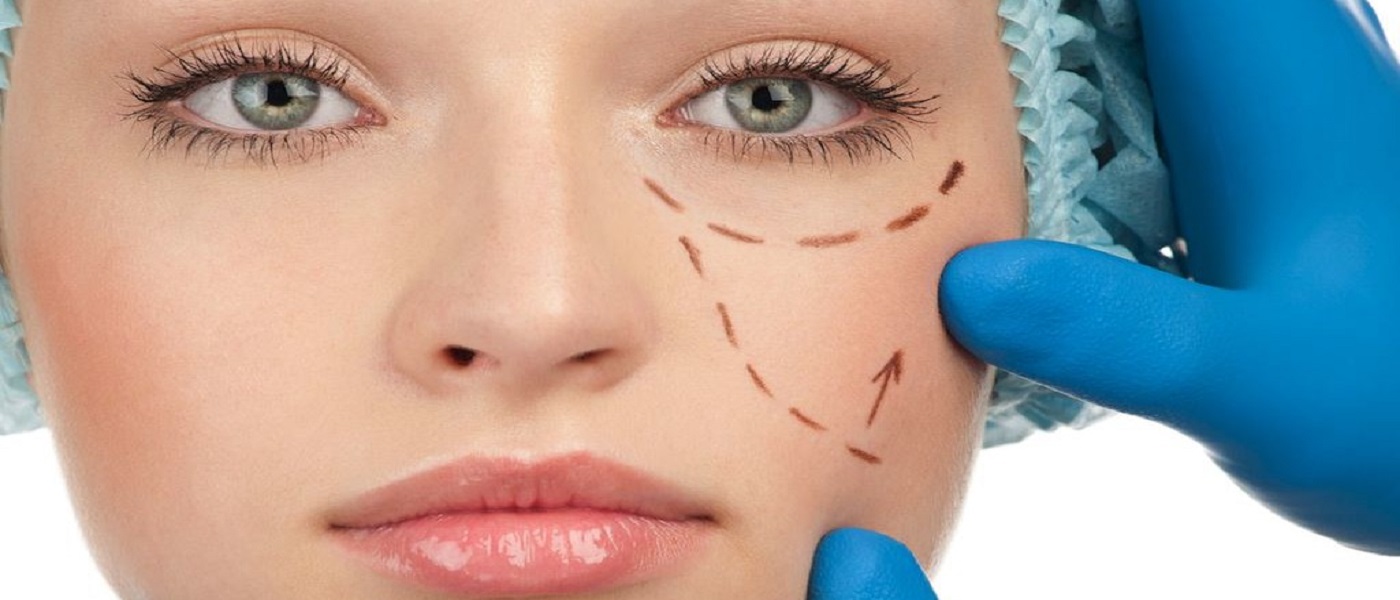
Is Cosmetic Surgery Allowed in Islam?
Being exposed to the ever-alluring representation of “A Perfect Body” in media through the picture of celebrities and actors, we inevitably grow more careful about our own body and try to compare ourselves with that unrealistic image that is made real for us. And the only remedy we find to get closer to that so-called norm is to change our appearances with the help of cosmetic surgeries.
Some people see a perfect correspondence between their physical features and inner confidence and instead of working on their inner abilities to elevate their character, try to make a better look. But there may be cases in which one is forced to undergo this kind of surgery out of necessity. What is Islam’s view about this matter on the whole? Are we allowed to have cosmetic surgeries or not? What are the conditions?
In what follows we will try to find the answers to these questions.
Islam’s View of Beauty
Beauty is a very relative concept and can at least be divided into two kinds: the beauty of the body vs. the beauty of the soul. In Islam, both of these aspects are given importance. However the latter is regarded as being superior to the former; Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) says in a narration that, “Allah does not look at your faces but your hearts and deeds” [1].
The beauty of your character and the purity of your soul which is born with you and then can be elevated by following Allah’s guidance is far more valuable than your beautiful body. What gets you closer to Allah is your pious deeds, since: “…Indeed the noblest of you in the sight of Allah is the most God wary among you” (49:13).
Nevertheless, Islam is a religion that pays careful attention to the matter of personal hygiene and appearance. We have many narrations that emphasize this issue. For instance, Imam Sadeq (AS) always recommended his followers to “be neat and orderly, since Allah is beautiful and loves that which is beautifully provided that it is lawful (Halal)”[2].
As the best example of practicing Islamic teachings in its ideal form, prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) always appeared in his best shape both in society and at home and in this way showed Islam’s concern about the matter of appearance and outer beauty.
What Does Islam Say about Cosmetic Surgery?
Having said all of the above, the idea of beautifying yourself through cosmetic surgery remains unresolved. According to most Islamic jurists, having this kind of operation is not forbidden (Haram) in itself, provided that it is done for medical treatment such as removing a burn mark or curing a deformed part of the body [3].
However, undergoing cosmetics surgery just for the sake of beauty and without any purpose of medical treatment is only allowed if it is done by a doctor of the same gender since it is not out of necessity. This is because in Islam patients can refer to a doctor of the opposite gender, only when no same-gender doctor is available, or his proficiency is lower than a doctor of the opposite gender[3]. To have a better view of “Islamic Etiquette of Looking” as well as the matter of Mahrams, you can refer to the related articles.
Conclusion
It has been proved by many psychologists that having a better life, more often, is not related to your outward appearance; in other words, being beautiful does not necessarily make you happy. Instead, working on the inner beauty and elevating your soul leads you to a beautiful perception. However, this does not mean that Islam gives no importance to personal appearance and physical beauty. Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) always rejected the notion of abandoning worldly pleasures altogether in favor of a solitary and monastic lifestyle [i].
Notes:
[i] Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) said: “ There is no monasticism in Islam” [4].
References:
- Mustadrak al Wassail, Vol 11, p. 264
- sul al Kafi , Vol 6 , p.442
- medical issue
- Na’aman Ibn Muhammad Tamimi Maqribi, Daaem Al-Islam, Egypt: Dar Almaaref ,Vol. 2, p.193
Share This Article

Narrations on Karbala and the pilgrimage of Imam Hussain (as) part2
Hadith 21: The Condition of Honor
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Whoever wants to be in the neighborhood of the Prophet (pbuh&HP) and next to Ali (AS) and Fatima (AS) should not leave the pilgrimage of Imam Hussain (AS).
Wasa'il al-Shi'ah, vol. 10, p. 331, p. 39
Hadith 22: Pilgrimage, Divine Duty
Imam Sadiq (as) said: If one of you observes the Ihram of Hajj for the entire of his life but does not visit Imam Hussain (as), he has left the right of the Messenger of Allah (PBUH&HP) because the right of Hussain (as) is a divine duty and obligatory for every Muslim.
Wasa'il al-Shi'ah, vol. 10, p. 333
Hadith 23: Karbala, the Kaaba of Perfection
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Whoever does not visit the grave of Imam Hussain (as) until he dies, his faith will be incomplete and his religion will be incomplete, and when he goes to heaven, he will be lower than the believers there.
Wasa'il al-Shi'ah, vol. 10, p. .335
Hadith 24: From Pilgrimage to Martyrdom
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Do not leave the pilgrimage of Imam Hussain (as) and recommend it to your friends and companions as well! May Allah prolong your life, increase your sustenance, and may Allah bless you alive and you will not die except as a martyr.
Wasa'il al-Shi'ah vol. 10, p. 335
Hadith 25: The Hadith of Love
It was narrated from Imam Sadiq (as) that he said: Whoever Allah wants good, will put the love of Hussain (AS) and his pilgrimage in his heart, and whoever Allah wants bad, will have him hate Hussain (AS) and anxious with his pilgrimage.
Wasa'il al-Shi'ah vol. 10, p. 388, Sea of Lights, vol. 98, p. 76
Hadith 26: A Sign of Being a Shiite
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Whoever does not visit the grave of Imam Hussain and dies as our Shiite and dies, is not our Shiite, and even if he is from the people of Paradise, he is the guest of the people of Paradise.
Kamel Al-Ziyarat, p. 193, Bihar Al-Anwar, vol. 98, p.4
Hadith 27: Ascension Platform
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Whoever visits the grave of Hussain (as) and has knowledge of the right of that Imam, Allah Almighty will register him in the highest rank.
Man la yahzurul Faqih, vol. 2, p.581
Hadith 28: The School of Knowledge
Imam Musa Kadhim (as) said: The least reward that is given to the pilgrim of Imam Hussain (as) on the banks of the Euphrates is that all his sins, before and after, are forgiven. Provided that he knows the right, honor and guardianship of that Imam.
Mustadrak al-Wasa'il, vol. 10, p. 236, quoting Kamil al-Ziyarat, p. 138
Hadith 29: Like the Pilgrimage of Allah
Imam Reza (as) said: Whoever visits the grave of Imam Hussain (as) on the banks of the Euphrates is like the one who has visited Allah.
Mustadrak al-Wasa'il, vol. 10, p. 250, quoting in full
Chapter Three: Ashura and Arbaeen
Hadith 30: Pilgrimage at Ashura
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Whoever visits Imam Hussain (as) on the day of Ashura, heaven will be obligatory for him.
Iqbal al-A'mal, p. 568
Hadith 31: Above Prosperity
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Whoever wakes up on the night of Ashura next to the shrine of Imam Hussain (as), on the Day of Judgment he will rush to Allah stained in his blood, like someone who was killed in Karbala next to Imam Hussain (as).
Wasaelu shiah, vol. 10, p.372
Hadith 32: Signs of Faith
Imam Hassan Askari (as) said: The signs of a believer are five:
1 Fifty prayers
2 Arbaeen pilgrimage
3 Ring in the right hand
4 Prostrating on the ground
5 Saying loudly the name of Allah, (Bismillah Rahman Rahim)
Wasaelu shia, vol. 10, p. 373, and also Al-Tahdhib, vol. 6, p. 52
Chapter Four: Torbat and Tasbih of Love
Hadith 33: His Porch
The Prophet of Islam (PBUH&HP) said: Know that the answer to prayer is under the dome of his shrine and healing is in his soil, and the Imams (as) are of his children.
Mustadrak al-Wasa'il, vol. 10, p.335
Hadith 34: Soil and Training
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Take your children with the soil of Hussain (as) (Karbala) because the soil of Karbala insures your children.
Wasaelu Shiah, vol. 10, p.410
Hadith 35: The Greatest Medicine
Imam Sadiq (as) said: The cure for any pain is in the soil (torbat) of Hussain (as) and it is the greatest medicine. Kamil Al-Ziyarat, p. 275 and Wasa'il al-Shi'ah, vol. 10, p. 410
Hadith 36: Torbat (soil of Karbala) and seven hijabs
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Prostration on the soil of Hussain (as) tears the seven veils.
Mesbah al-Muttahid, p. 511, and Bihar al-Anwar, vol. 98, p. 135
Hadith 37: Prostration on the Soil of Love
Imam Sadiq (as) did not prostrate on the ground except on the soil of Hussain (as) and he did this in violence for the sake of Allah.
Wasailu shiah vol. 3, p.608
Hadith 38: Rosary with the Soil of Karbala
Imam Sadiq (as) said: Prostration on the soil of Karbala can light up to the seventh earth, and whoever has a rosary from the soil of the shrine of Hussain (as) with him, is a truthful person, even if he says nothing.
Man la yahzurulFaqih vol 1 p 268
Hadith 39: Healing Soil
Imam Kadhim (as) while narrating a hadith announcing his death, said: do not take anything from the soil of my grave to seek blessings, because it is forbidden for us to eat any soil except the soil of my grandfather Hussain (as), Allah Almighty has healed only the soil of Karbala for the Shiites and our friends.
Jami ahadith, vol. 12, p.533
Hadith 40: One of the Four Needs
Imam Musa ibn Ja'far (as) said: Our needs are four things:
1. Prayer mat on which prayers are offered.
2. Rings on the finger
3. Toothbrush with which to brush teeth
4. A rosary from the shrine of Imam Hussain (as) Tahdhib al-Ahkam, vol. 6, p. 75
Read More

How Has Imam Hussain’s (AS) Uprising Inspired Humankind? Part 1
Imam Hussain (AS) is one of the important figures in Islam whose brilliant and lofty character together with his inspiring movement has been praised by many famous characters of the world. In this regard, Mahatma Gandhi said that: “My admiration for the noble sacrifice of Imam Hussein (AS) as a martyr abounds, because he accepted death ..., but did not submit to unjust authorities. I learned from Hussain how to attain victory while being oppressed.” [1]. Antoine Bara, a thinker, scholar, Christian and Syrian who wrote a book titled, “Imam Hussein in Christian ideology,” said that: “I am a Christian but call on humanity to follow the holiness of Imam Hussein as he is the conscience of all religions.” [2]. These quotes and others indicate that Imam Hussain (AS) is not an exclusive role model for Shi’a or Muslims, but belongs to the whole world. One might ask in what ways is Imam Hussain’s (AS) uprising an inspiration for human beings. We try to explain that through the following lines.
Imam Hussain (AS) Confronts the Oppressive Corrupted Regimes
Yazid’s reign was corrupted and illegitimate from the beginning. According to the peace treaty made between Imam Hassan (AS) and Mu’awiyah, the latter was forbidden to designate anyone as his successor after his death. But after the martyrdom of Imam Hassan (AS), Mu’awiyah broke the treaty. He appointed his son Yazid as his successor because he thought no one would be courageous enough to object to the decision of caliph. Hence, Yazid became caliph illegally after the death of Mu’awiyah [3]. Besides, according to historical resources, Yazid had a corrupted immoral character. He dared to act against Islamic rulings openly and perform forbidden deeds (Haram) in Islam publicly [3].
Imam Hussain (AS) was observant and aware of Yazid’s acts and intention. So, he refrained from pledging allegiance to Yazid. Moreover, oppression, tyranny, unjust use of public property, etc. had made life miserable for people [4]. Imam Hussain (AS) believed that Yazid’s manner and governing style was obviously against Islamic teachings and would eventually alter and spoil Prophet Muhammad’s (PBUH&PH) Sunnah. Hence, he stood up against Yazid to prove that his reign was illegitimate and to unravel the truth. Therefore, he (AS) said that he would never take the oath of allegiance to Yazid, even if there would be nowhere safe on the earth for him to go [5]. He never intended to take on the leadership and come to power, instead aimed at eliminating injustice and corruption.
Achieving Leadership, Not at Any Price
One might wonder why Imam Hussain (AS) did not pledge allegiance to Yazid to calm down his hostility so that he would have more time to make plans and find more companions to defeat Yazid. The reason was that Yazid’s behavior and deeds were too far from true Islamic principles and moral values such that Imam (AS) could not ignore them. Moreover, he (AS) did not want to play a trick as it is denounced in Islam.
Imam (AS) had other possibilities to defeat Yazid and take over the leadership, but he (AS) refused to do so. Through his missionary in Kufa, Muslim ibn Aqil, Imam (AS) could kill Ubayd Allah ibn Ziyad [i] before the battle of Karbala and before the enemy declared war against them. But, as a man who had stood up for justice, he did not act unfairly. Imam’s (AS) reaction was in the same manner as well; before the battle started when the enemy was fewer in number and easier to defeat, one of his (AS) companions recommended fighting them. He (AS) replied that he would rather defend if a war were imposed on him instead of initiating it. Moreover, when the enemy was impatient to start the battle, he (AS) did his best to prevent it by negotiating and bringing awareness to them by revealing the truth [4].
These examples demonstrate that Imam (AS) did not want to reign at any price; the same was true for other Infallible Imams (AS). This is of the traits of true divine leaders; unlike oppressive unjust powers. They never take the lead, whatever the cost.
Up to now, we found out about two reasons that make Imam Hussain’s (AS) uprising a worldwide inspiration. Firstly, one should be alert and sensitive to what happens around him\her. Then, to take the right action for the sake of justice and humanity. Secondly, even if one holds a noble intention, it does not mean that he\she is allowed to achieve that by any means; the end does not justify the means.
Imam Hussain’s (AS) movement has other lessons for human beings that we will discuss in the second part of this title.
Notes:
[i] The governor of Kufa during the reigns of Yazid, who executed Aqil, sent troops to intercept Imam Hussain (AS) when he arrived near Kufa and was one of the leaders of the battle against Imam (AS) in Karbala.
References:
- http://realiran.org/world-personalities-quote-imam-hussain/
- https://standwithdignity.org/article/antoine-bara-you-shia-do-not-appreciate-the-value-of-imam-hussein/
- https://www.al-islam.org/the-hidden-truth-about-karbala-ak-ahmed/chapter-13-muslim-empire
- https://salamislam.com/lifestyle/imam-hussain-embodiment-universal-moral-law
- M. Majlisi, “Bihar al-Anwar,” Dar Ihya al-Turath al-Arabi, Beirut, vol. 44, p. 325
Read More

