

What is the History of Ramadan?
Ramadan is the 9th month of the Islamic calendar. The root of the word in most of the dictionaries refers to strong heat or burnt earth. Some commentators use this meaning to refer to the heat and hardship that people endure during Ramadan fasting. However, there is another meaning for the root of the Arabic word “Ramadan” which refers to the clouds and the rain at the end of summer and beginning of fall. [1] Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) says: “Indeed, it is called Ramadan because it burns the sins”. [2] In this narration both meanings can be adopted, since based on the first meaning it burns the sins, and based on the second meaning, it quenches the fire that is the consequence of sins.
Contemplating on the verse of the Quran “The month of Ramadhan is one in which the Quran was sent down as guidance to mankind, with manifest proofs of guidance and the Criterion…” (2:185), one can conclude that the second meaning that was mentioned for the word “Ramadan” is more suitable to describe this month; a month in which blessings and bounties of Allah (SWT) shower on His servants. One of those blessings as mentioned in the above verse is the Holy Quran which was revealed in Ramadan on the greatest night of the year: “Indeed We sent it down on the Night of Ordainment” (97: 1). In another verse, Allah (SWT) mentions, “We sent it down on a blessed night.” (44:3)
The three mentioned verses have some points that can help us think and discover if the month of Ramadan became a holy month after Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) brought Islam, or was it always a holy month throughout history?
What does the Quran tell us about the history of Ramadan?
As mentioned in the above verses and other verses of the Quran, Allah (SWT) tells us that:
1- The Quran was revealed in the Holy month of Ramadan. (2:185)
2- The Quran was revealed on the night of decree. (97: 1)
3- The night of decree is so high in a position that no normal human being can understand its status and value: “And what can make you know what is the Night of Decree? The Night of Decree is better than a thousand months.” (97:2-3)
4- According to verse 44: 4, every firm ruling is dispatched on that night. These rulings are the decrees concerning the way the affairs of the world should run until the same time next year. Such a concept which is related to the creation should have been an eternal matter and could not have come about just by the advent of Islam.
By doing simple math on the above verses, we can conclude that before the Quran was revealed, the night of decree existed as a blessed night, and by Allah’s will the Quran was revealed in this blessed night. Therefore, Ramadan always existed as a blessed month in which the night of decree has always been a prominent night.

History of fasting
The word fasting is mentioned a few times in the Quran when Allah orders Prophet Zachariah (PBUH) and Saint Mary to avoid talking to people: “Then if you see any human, say, ‘‘Indeed I have vowed a fast to the All-beneficent, so I will not speak to any human today.’’ (19:26)
The above verse shows that there have been different traditions of avoiding specific things, which has been called fasting. However, the verse of the Quran that makes fasting an obligation on Muslims says: “O you who have faith! Prescribed for you is fasting as it was prescribed for those who were before you, so that you may be Godwary.” (2:183)
The commentators of the Quran have disagreed about the purport of this verse. Some argue that the phrase as it was prescribed for those who were before you is referring to the concept of fasting only. It means that the previous nations were told to fast like you are told, however, the verse is silent about the time or the way of their fasting. Others, say that as it was prescribed for those who were before you means that the fast of Ramadan was prescribed for them exactly in the same way that it is prescribed for you.
Looking into the rules and descriptions of fasting in Christian and Jewish traditions would certainly support the first view since neither of these religions have fasting in Ramadan as part of their traditions. However, some commentators, quoting Hasan al-Basri have argued that the verse refers to Christian fasting which was originally ordained to be in Ramadan but they changed it over time. They say that fasting during the Lent season which in Christian tradition is related to the testing of Jesus in the wilderness is not the original concept of fast in Christianity. Rather, what was originally prescribed for them was the fast of Ramadan, but since as a lunar month it circulated over different seasons, the leaders of the church decided to fix it in the spring and add ten days to it as an atonement for such a change. It was then called Lent and related to the 40 days of Jesus’s tests in the wilderness.
However, we have to regard this as an odd view, since nothing in history can support such a development. Thus, as most of the commentators say, as it was prescribed for those who were before you, means that people of previous Scriptures were also told to fast, although not exactly in the month of Ramadan.
However, there is a third view here which can be regarded as a combination of the above two views, and as a view that makes the sanctity of Ramadan of a primordial nature. It is narrated from Imam Sadiq (AS) that “Allah (SWT) has not made fasting of Ramadan compulsory on any nation before Muslims.” He was asked about the interpretation of the verse “as it was prescribed for those who were before you”, where he replied: “Allah had made fasting of Ramadhan compulsory on the Prophets before you, but He prioritized this nation by it and made fasting an obligation on the Prophet and his followers.” [4] This means although fasting of Ramadan was not prescribed for previous nations, the past prophets used to honor Ramadan by fasting during the month. Something similar to this is reported about Hajj too. It is narrated that although Hajj is an exclusive obligation of the nation of Islam, however, prophets of the past nations including Moses and Jesus performed Hajj.
It is also narrated that the first Prophet who fasted was Prophet Adam: “when Adam ate the fruit of the forbidden tree, that fruit remained in his stomach for thirty days, and it was then that Allah made the thirty days of fasting obligatory on Adam and his generation.” [5]
In conclusion, what could be firmly said, is that fasting is not an obligation specific to Muslims only. All nations who received Scriptures were also told to fast like Muslims are told to fast, although the details about how and when they must fast may have been different.
References:
- Ramadan
- Mizan al-Hikmah, Hadith No. 7441
- Man- la- Yahzuruhul faqih, vol. 2, p. 99
- Man- la- Yahzuruhul faqih, vol. 2, p. 74
- Imam Fakhr-e Razi, Tafseer Surah Al-Baqarah, P. 59
Share This Article
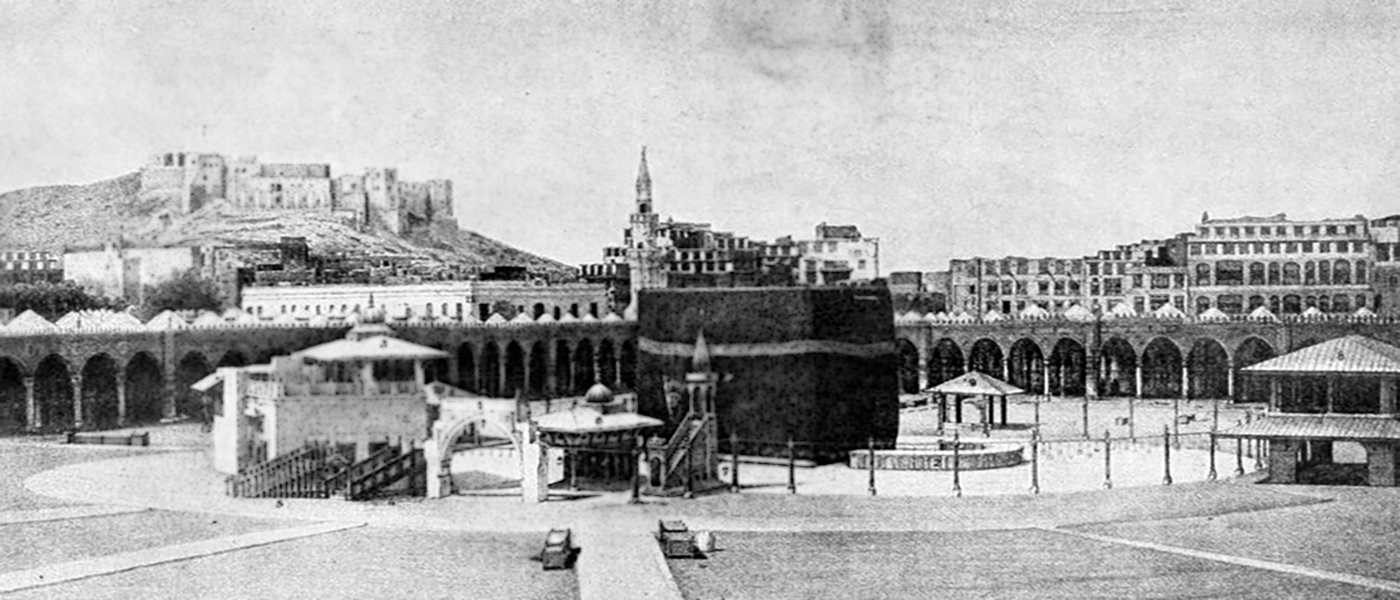
What is the History behind Building the Kaaba?
The word Kaaba means cube in Arabic, and it refers to the square-like building in the holy city of Mecca, which is covered with a silk and cotton veil. It is the most sacred site for Muslims, and millions of people travel to visit that as a pilgrim each year.
Many people think that Kaaba was built at the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) and with the advent of Islam. However, history has a different narration about which we are going to talk in this article.
1. The First People who Built Kaaba
The first person who built Kaaba was Adam (PBUH), and it was remained unharmed until the great flood at the time of Noah (PBUH) [1], which caused it to be partially damaged. Afterward, the structure of the Kaaba was reconstructed by prophet Abraham (PBUH) and his son, Ishmael, under the command of Allah. The Quran has narrated this story in this verse:
As Abraham raised the foundations of the House with Ishmael, [they prayed]: 'Our Lord, accept it from us! Indeed, You are the All-hearing, the All-knowing. (2: 127)
2. Kaaba Between Abraham (PBUH) and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
The son of prophet Abraham (PBUH), Ishmael (PBUH), and a tribe named Jorohom were the guardians of Kaaba after the demise of prophet Abraham (PBUH). This magnificent building stood upright until that Jarhim tribe, and then a tribe named Amaaleh rebuilt the square-shaped holy place [2]. Years after, one of the predecessors of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) named Qusai Bin Kelab, made a wooden structure to protect the building and neighbored it with another building Called Dar-ol Nadvah, which was the governor's state. Then he asked each Quraysh tribe to locate their houses mirroring one side of the Kaaba, to build a circle around it. Some say that Kaaba was once ruined in flood before the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP), but that again is not proven [3].
3. Kaaba and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
When Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was chosen as the Messenger of Allah, Kaaba was considered a holy place. Some reference books say that Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) took part in the reconstruction of the Kaaba after the flood. Also, there was a fight between the Arab clans about where to locate the Black Stone, and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was chosen as the trustee of all clans to locate the holy stone on the eastern side's edge. (4) Kaaba was filled with idols and statues when Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) left Mecca because of the severe tortures and problems the Arab clans made for him and his followers. Even years before, Kaaba was a place to worship the idols.
When Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) gathered his followers and returned to Mecca, he ruined all those idols with the help of his first follower and friend, Imam Ali Ibn Abi Talib (AS). Kaaba became a center of performing Hajj and the Qibla [i] of the Muslims. The Dome of Rocks (Qubbat al-Ṣakhrah ) was the first Qibla of Muslims, but Allah inspired Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) to change it toward the Cubic Kaaba.
4. Kaaba After Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
Kaaba has been reconstructed many times after the demise of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP), but the cubic shape of the building has never been changed. Now, the Saudi Arabian Government is responsible for preserving this sanctuary, though it belongs to all Muslims and all nations. There are many different parts and holy sites around Kaaba, like the Black Stone, the Iraqi corner, the Kiswa, or the black covering, which we are going to discuss in our next articles.
Notes:
[i] Qibla is the direction to which all Muslims say their prayers.
References:
- Arzaghi, Abu Valid Kaaba News and What happened to that, Vol. 1, P 68.
- Seyyed Hashem Bahrani,Tafsir Al-Burhan Vol. 1 P 301 Hadith 36.
- Rasouli Mahallati, Hashim Analytical History of Islam (2), (1991) Tehran, Iran.
- Guillaume, A. (1955). The Life of Muhammad. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 84–87.
Read More

Four Questions You Might Ask about Hajj
Hajj is the most glorious manifestation of Muslims' unity, where millions of Muslims say "Yes" to the divine invitation and come together around the Kaaba in Mecca. You might have already read about the philosophy of Hajj and the details around it. Here, we answer some questions that you might want to know more about Hajj.
1. Who Built Kaaba and Why?
According to most of the references, Kaaba was first built by Adam (PBUH). Later on, in the era of Noah (PBUH), when a flood occurred throughout the whole Earth, Kaaba was not completely ruined but damaged. Some years later, the location of the Kaaba was shown to Prophet Abraham (PBUH) [1]. He had the mission to reconstruct Kaaba with the help of his son Ishmael (PBUH) [2]: "As Ibrahim raised the foundations of the House with Ishmael, [they prayed]: 'Our Allah, accept it from us!'" (2:127). According to the verses of the Quran, the reason to build Kaaba was to found a place of reward for humankind and a sanctuary [3] where people come to worship Allah: "And proclaim the Hajj to people" (22:27).
2. Who Can Perform Hajj?
As one of the practical principles of Islam, Hajj is obligatory only once in one's lifetime, if he/she fills some conditions that consist of:
To be of sane mind;
To have reached puberty;
To be free;
To have financial means (called Istita'ah), i. e., to have enough money to support oneself and his/her family on this journey;
To be in good physical condition, i. e., Hajj is not obligatory for the sick, the extremely old who cannot even move or those who are either unable or would face severe hardship;
To possess means for a safe trip.
If one fulfills all these conditions, then it is mandatory for him/her to perform Hajj.
3. Why Is the Phrase "Labbayk" Repeated?
Labbayk means "I am abiding upon your compliance" and is used to answer in the affirmative, to agree with, and accept an invitation [4]. The phrase Labbayk is one of the obligations during Hajj by saying which one can enter the state of Ihram [5].
According to Imam Kazim (AS), Allah Almighty will forbid the Hellfire to those who entered the state of Ihram during Hajj. Saying "Labbayk Allahumma Labbayk" is actually an answer to Almighty Allah in return to what He has said." [6]. In another narration, it is stated that this phrase is an answer to the call of Almighty Allah (22:27) to perform Hajj [7].
4. How Is Hajj an Expression of the Beliefs of Islam?
Hajj is the most significant congregation of Muslim society from all over the world that manifests how religion and society are linked. The rituals that must be performed during Hajj and the words that should be repeated remind us of:
Monotheism: the fundamental axiom of Islam that implies the existence of one creator, a divine source, and a higher power, and His absolute uniqueness and singularity;
Denial of all other powers: by testifying to monotheism, every other power, whether eastern or western, will be rejected. That means those who believe in monotheism won't be indifferent about the injustice, cruelty, and oppression that world powers inflict on their people or other countries;
The importance of unity: millions of pilgrims who have left behind the religious conflicts, and follow the same intention, perform the same actions, and wear the same outfit, represent the glorious Islamic unity;
International peace and amity: bringing together the people of various nationalities, skin colors, languages, and sects and considering all of them equal except for their degree of piety, encourage brotherhood and peace in the whole world.
Here we discussed some of the common questions about Hajj, but there is much more to know. If you have any questions in this regard, do not hesitate to write to us.
References:
- The Quran (22:26)
- N. Makarem Shirzi, “Tafsir Nemooneh”, vol. 14, p. 67.
- The Quran (2:125)
- Hajj
- M. Bahjat, "Manasik Hajj va Umrah", p. 90.
- Shaykh H. Amili, “Wasa'il al-Shia”, vol. 12, p. 375.
- Shaykh H. Amili, “Wasa'il al-Shia”, vol. 12, p. 377.
Read More

