

Imam Mahdi (AS) The Last Savior
Mahdi (as) is a messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH& HP) who will appear while Jesus Christ (Prophet Isa-ibni Maryam) accompanying him and will lead the believers to rule the world and fill it with justice and peace. This is what the Quran says:
And We wanted to confer favour upon those who were oppressed in the land and make them leaders and make them inheritors. (Al-Qasas 28:5)
Who is Mahdi (as)?
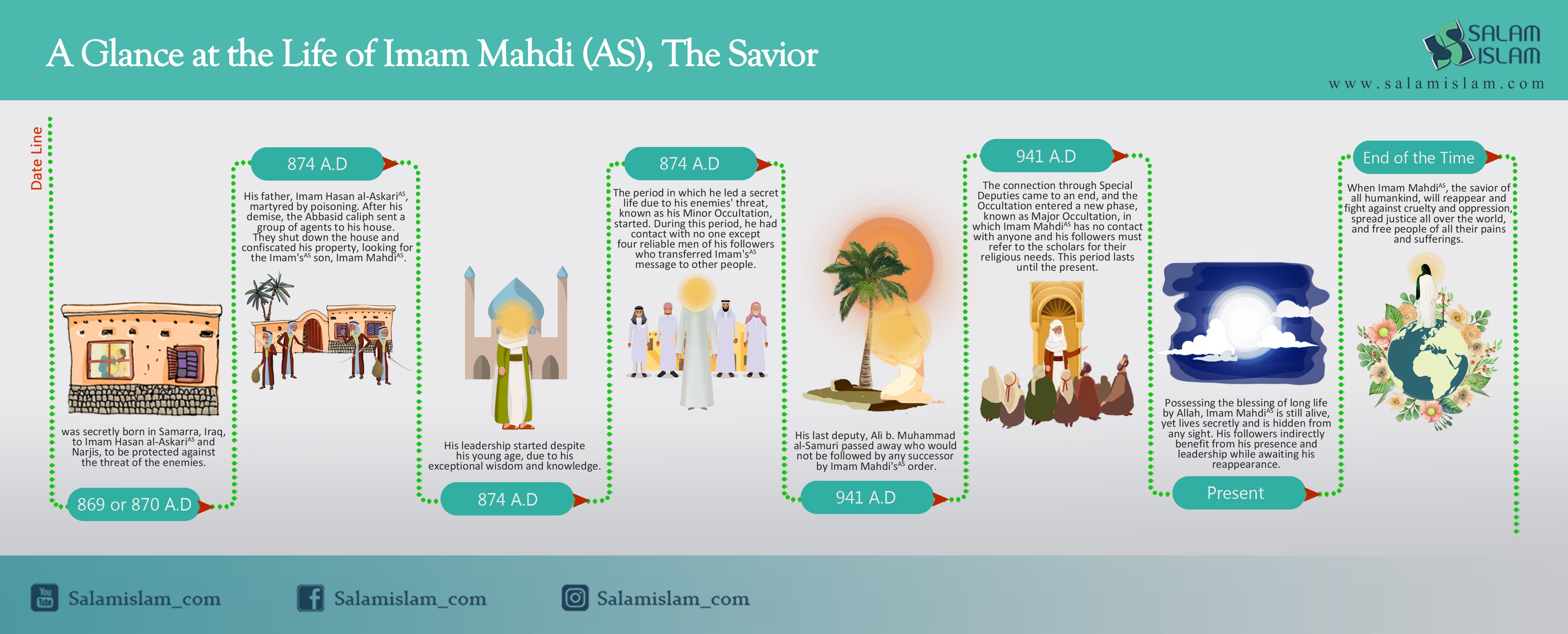
The name Mahdi is derived from the Arabic root h-d-y, commonly used to mean "divine guidance". Though Imam Mahdi features in both Shia and Sunni understandings of Islam, they differ in his attributes and status. Among Twelver Shi’as, Mahdi is believed to be the son of the eleventh Imam, Imam Hasan al-Askari (d. 874), and is said to have been on divine occultation (ghaybat) by God’s will. However, the Sunnis assert that he (Imam Mahdi) is a descendant of Lady Fatimah (SA), the daughter of the Prophet Muhammad, and it is unknown whether he was born or not.
What is the View of Muslims About Mahdi (as)?
According to our belief, one of the most extraordinary acts of worship is to wait for the promised saviour, and this waiting means trying to provide the conditions for his reappearance.
In the Shi'a Islam, or the school of Ahlul-Bayt, the eschatological Mahdi was commonly given the epithet al-Qa'im, which can be translated as “he who will rise”, signifying his rise against tyranny in the end of all times. Distinctively Shi'a is the notion of the temporary occultation of Imam Mahdi, whose life has been prolonged by God’s will.
As in above mentioned, the Sunnis also believe in the promised Mahdi and many hadiths about him have been narrated in their books. Abu Dawood quotes Prophet Muhammad (PBUH & HP) as saying: " Mahdi will be from my household, from the descendants of Fatimah”. And another hadith states: “Even if only one day remains [until the doomsday], God will lengthen this day until He calls forth a man from me, or from the family of my house, his name matching mine and his father's name matching that of my father. He will fill the Earth with equity and justice just as it had previously been filled with injustice and oppression”. (Furnish, 2005, p. 14) According to narrations before the arrival of Imam Mahdi, the earth would be filled with chaos. While divisions and civil wars, moral degradation, and worldliness would be prevalent among people, injustice and oppression would be rampant throughout the world. The Dajjal (The Anti-Christ) would appear and will spread decadence and corruption in the world. With an army bearing black banners, which would come to his aid from the east, Imam Mahdi would confront the Dajjal. Jesus would pray behind Imam Mahdi and then will kill the Dajjal. The Sufyani, another representative of the forces of the dark, also features in the traditions. He will rise in Syria before the appearance of Imam Mahdi. When the latter appears, the Sufyani, along with his army, will either be swallowed up en-route to Mecca by the earth by God's command or defeated by Imam Mahdi.
What Role does he have in the Future of Humanity
In Imamiyyah (Twelver Shiism), the largest Shi’a branch, believing in the messianic imam is not merely a part of the creed, but is the pivot. For the Twelver Shi'a, Imam Mahdi was born but disappeared after a while, and he would remain hidden from humanity until he reappears to bring justice to the world at the end of time, a doctrine known as the Occultation. This Imam on occultation is the twelfth imam, named Muhammad, son of the eleventh Imam, Hasan al-Askari. According to the Twelvers, the Mahdi was born in Sammara around 868, though his birth was kept hidden from the public. He lived under his father's care until 874 when the latter was killed by the Abbasids.
Shi'a scholars have argued that the prolonged lifespan of Imam Mahdi Mahdi is not at all unreasonable given the longevity of the Prophet Noah, Khidr and Jesus, as well as secular reports about long-lived people. According to scholars Imam Mahdi is viewed as the restorer of true Islam, and the restorer of other monotheistic religions after their distortion and abandonment. He establishes the kingdom of God on earth and Islamizes the whole world. As a matter of fact, in their true form, it is believed, all monotheistic religions are essentially identical to Islam as "submission to God." It is in this sense, that one should understand the allegation that al-Mahdi will impose Islam on everyone. His rule will be paradise on earth, which will last for several years until his decease.[1]
References:
- (Sachedina, 1981, p. 176-178)
Share This Article

Imam Hussain (AS), Fight or Peace?
After Imam Ali (AS) was martyred, Imam Hassan (AS) took over as his successor who like his father fought against Mu’aviah but he couldn’t defeat him because his army was not sufficiently loyal. His reliable followers were inadequate and he feared that they could be killed in the battle. Thus, Imam Hassan (AS) made a peace treaty with Mu’aviah, under the duress against his own will.
Mu’aviah became the Caliph under specific circumstances. For instance, he wasn’t allowed to choose the next Caliph and his son (Yazid) couldn’t be his successor. On the other hand, when Mu’aviah died, Imam Hussain (AS) was opposed to and fought against Yazid and he and his followers were brutally martyred. Both Imam Hassan (AS) and Imam Hussain (AS) had few collaborators/ associates/ helpers; however, this did not stop him from protesting against Yazid and his tyranny.
One of the most controversial questions about Imam Hussain (AS) is that why he did not make peace with Yazid just like his bother did with Mu’aviah?
The Wrong Belief
It is worth noting that it would be so irrational to think that Imam Hussain (AS) had a different disposition from Imam Hassan (AS), for example one was more of a diplomat while the other was more of a fighter. In fact the objective conditions at the times of two Imams were rather different hence, their approach apparently differed.
1. Mu’aviah was willing to make peace with Imam Hassan (AS) but Yazid wasn’t like his father. Mu’aviah did not want to fight against either Imam Hassan (AS) or Imam Hussain (AS) and they were not prepared to do so. Once the governor of Medina wrote to Mu’aviah that Hussain (AS) does not want to take over the kingdom for now but he may do in the future. Mu’avia wrote to the ruler:
Leave Hussain (AS) and do not bother him because we don’t want to conflict with him while he is in peace with us (1)
On the other hand, when Yazid became the Caliph, he ordered the governor of Medina to make Imam Hussain (AS) to either obtain the oath of loyalty (to the Caliphate of Yazid) or failing that, kill Imam Hussain (AS), cut off his head and send it to Yazid.
2. In public Mu’aviah was, at least superficially, a pious person who would not commit sins or harm innocent people. Sometimes even the followers of Imam Ali (AS) had doubts about the impiety of Mu’aviah. While Yazid had no reservations, he would commit sins in public including drinking wine, playing with dogs and monkeys and etc. As in this regard Imam Hussain (AS) said:
Yazid is an alcoholic person and kills innocent people and does sins in public, so a person like me wouldn’t accept a person like him as their king (2)
3. Mu’aviah was a very powerful king with strong army but Yazid was not as clever and strong.
4. The loyalty of many of Imam Hassan’s (AS) followers was questionable. Some abandoned him and some others tried to kill him or even surrender him to Mu’aviah. But the companions of Imam Hussain (AS), as he himself said, were of a better and more loyal caliber. (3)
5. Mu’aviah was among the companions of the Prophet (PBUH) which earned him the respect of Muslims in general whereas Yazid was not a companion of the Prophet (PBUH) was so important to Muslims in that time and people would respect him so much. But Yazid wasn’t a companion of the Prophet.
6. Mu’aviah’s sister (Um Habibah) was the Prophet’s wife. Since the prophet’s wives are called ‘’the mothers of the believers ‘’; therefore, Mu’aviah was called “the uncle of the believers”. Yazid, however, did not have such status.
7. Although he did not meet any of his commitments that he had already made, Mu’aviah could say that he is legally the caliph because of the peace agreement between him and Imam Hassan (AS) because Yazid could not claim such legitimately.

Imam Hussain (AS) and respect to the Peace
Some people think that Imam Hussain (AS) didn’t agree with his brother in making peace with Mu’aviah however because of his respect for his brother, he observed the peace treaty and did not oppose Muaviah. However, this view about Imam Hussain is not right.
If we assume/Supposing that Imam Hussain (AS) did not actually agree with his senior brother, he could fight against Mu’aviah; because, the latter broke his agreement that he had made with Imam Hassan (AS), when he made his son, Yazid, his successor and Imam Hussain (AS) had no agreement with Muaviah however the circumstances of Imam Hussain were unsuitable for an uprising against Muaviah.
References
- Bihar al-anvar, Majlesi, vol.44, pg.212
- Maghtal al-Hussain (AS), Abd ar-Razzaq al-Muqarram, pg.129
- Musnad al-Imam ash-Shahid, al-Atarodi, vol.2, pg.4
Read More

Was Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) a Violent Man?
How high is the power of his religion that even 1400 years after his death, some people try to tarnish his personality? The religion of Islam brought and spread by Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) is gaining more and more followers and lovers. This vast amount of conversion to Islam has negative consequences for the materialist and capitalist rulers in the world. By following Islam, people learn to stand for their rights and oppose the tyranny of oppressors. The rules of Islam question the rules made by the oppressor rulers in different societies.
Therefore, the increase in the number of people who embrace Islam and the Islamic lifestyle frightens those tyrant rulers, and they make plans to decay the status of Islam in different ways. One of the plans that they have been applying throughout the past decades was to introduce a violent personality of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP). In this text, we will study the conduct of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) and the representation of his manners and behaviors in the Quran to review his kind and merciful character better.
Characteristics of a Preacher as Described by Allah Almighty
Sending messengers by Allah Almighty to people implies His deep care for them and His will to guide them toward prosperity. But His messengers were supposed to follow specific rulings in their invitation of people toward Him. Being kind and merciful to people is one of the characteristics that Allah Almighty ordered His messengers to observe.
When Allah was sending Prophet Moses and Aaron (PBUT) to Pharaoh, who claimed to be Allah, He told them that if they want their words to be heard, they should speak to him in a lenient manner: “Both of you go to Pharaoh, for he has indeed rebelled. Speak to him in a soft manner; maybe he will take admonition or fear.’” (20: 43-44)
Prophets were commanded to be patient with their people and never become angry at them. The only prophet mentioned in the Quran who became disappointed of his people and left them was Prophet Yunus (AS), who was punished by Allah for his impatience and disappointment: “And [remember] the Man of the Fish, when he left in a rage, thinking that We would not put him to hardship. Then he cried out in the darkness, ‘There is no god except You! You are immaculate! I have indeed been among the wrongdoers!’” (21: 87)
Therefore, when Allah Almighty’s criterion in choosing His messengers is mercifulness and kindness, how can He keep a violent prophet among His servants?
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) as Described in the Quran
Like any other prophets, Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) had the characteristics of a chosen prophet. He was kind and merciful by the Mercy of his Lord as mentioned in the Quran: “It is by Allah’s mercy that you are gentle to them; had you been harsh and hardhearted, they would have surely scattered from around you...” (3: 159)
But the kindness and mercy of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) throughout his call toward Allah (SWT) come to a point where Allah Almighty tells him to be easier oh himself: “You are liable to imperil your life [out of distress] that they will not have faith.” (26: 3)
When Allah Almighty sees the unfriendly behavior of people toward Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP), He starts to point out and count Prophet’s kindly manners to people: “There has certainly come to you an apostle from among yourselves. Grievous to him is your distress; he has a deep concern for you and is most kind and merciful to the faithful.” (9:128)
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was not only merciful to the people in Arabia, but he was sent to be a caring for all human beings in all times: “We did not send you but as a mercy to all the nations.” (21: 107)
All presentations of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) in the Quran are about his great kindness and his caring personality. Allah describes his manner and behavior as being the perfect example for humankind: “and indeed, you possess a great character.” (68: 4)
Was Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) Kind to His Enemies?
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was so kind to people that even if they harmed him, he did not reply to them violently. It is narrated from Ibn Mas’oud, who said: I saw people hit the prophet and made his face full of blood, but while he was rubbing the blood off his face, he prayed, “O Lord! Please forgive my people as they are ignorant.” [1] In the early years of his prophethood, people kept harming the Prophet (PBUH&HP), but instead of cursing them, the Prophet (PBUH&HP) kept praying for their guidance.
The Prophet (PBUH&HP) never violated the heads of Quraish for their aggravation and torture and kept asking Allah Almighty to forgive them, until Allah Almighty by His knowledge of their persistence in remaining infidels sent him the following verse: “It is the same for them whether you plead for forgiveness for them, or do not plead for forgiveness for them: Allah will never forgive them. Indeed Allah does not guide the transgressing lot.” (63: 6)
Allah Almighty then described the characteristics of Muslims in a way that at the same time that they should not oppress anyone, they shouldn’t undergo any oppression, and defined the real Muslim society with the following manners:
“Muhammad, the Apostle of Allah, and those who are with him are hard against the faithless and merciful amongst themselves. You see them bowing and prostrating [in worship], seeking Allah’s grace, and [His] pleasure...” (48: 20)
Like any other human being, despite his great and kind personality, Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) had to react in different manners with different people. Therefore, if he had any serious encounter with people, it was not because of his violent attitude, but because of the correct reaction that any sane and smart man should have in facing different people.
References:
- Sahih Bukhari, Vol. 9, P. 20.
Read More

