

How Does Hajj Unite all Muslims?
Unity between Muslims is considered as a crucial matter in Islam. Thus, the Quran compares discordance and disunity among Muslims to “a pit of the Fire”: "And hold firmly to the rope of Allah all together and do not become divided...And you were on the edge of a pit of the Fire, and He saved you from it." (3:103). Looking at the former nations, we find them honored and glorious when they were united, but disgraced and vulnerable when they fell apart [3]. Hajj, as one of the obligatory rituals in Islam, is one of the ways which encourages unity among Muslim nations. Let’s see how.
Every Muslim is Welcomed to Hajj, No Exception!
There is no other ritual, social, or political program in Islam greater than Hajj, where every Muslim from any corner of the world finds the chance to approach others and communicate with them freely.
Besides, it provides the opportunity to strengthen the emotional, social, and religious bonds with other Muslims. Hajj is a social kind of worship that represents the glorious Islamic unity through its numerous participants of various nationalities, skin colors, languages, and sects who are like brothers (49:10). They have left behind the religious conflicts, and follow the same intention, perform the same actions, and wear the same outfit.
Hajj Brings Muslims Power
In Surah Ma’idah, it is stated that coming together around Ka’aba makes Muslims powerful (5:97). In other words, the aim of Hajj for Muslims is not just performing some physical actions. It is to bring Muslims of different races and origins together to get acquainted, communicate with each other, initiate political, economic and cultural relations, and find themselves closer to each other despite their many differences.
Besides, Islam calls “every” Muslim to Hajj, which means that everyone, regardless of origin and skin color, is invited to the land of Allah. It reminds us of what the Quran says; that there is no superiority except rightfulness and the most righteous, is the noblest in the sight of Allah (49:13). This is an important message, especially for the less powerful Islamic nations, causing them to feel more confident and encouraging them to communicate with other Muslims, which ultimately results in a more united Muslim society.
Muslims Are Like the Hands which Help Each other
In a discourse that Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) has given during one of his Hajj pilgrimages, he described Muslims as brothers, and like a single hand (a united community) when facing the enemies [2]. Emphasizing brotherhood among Muslims during Hajj shows that this ritual was a good representation of unity. Thus, Muslims are expected to support each other and be close to each other as they are during Hajj.
Two Axes of Solidarity in Hajj
During Hajj, Muslims learn and practice solidarity in two main areas:
1. Ideology and Principles
During Hajj, Muslims can exchange ideas with Muslims of other sects. In the early years of Islam when non-Muslims also went to Mecca for their religious rituals, Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) took this opportunity to introduce Islam to them and exchange ideas with them to spread his message and find followers in other cities, too. In Hajj, many misunderstandings and ideological conflicts can be discussed among Muslims, and the real beliefs of different sects about the others can be clarified. Hence, the wrong prejudgments and hostilities can be rectified. According to Imam Sadiq (AS), Hajj is a means to gather all Muslims from east to west to let them get acquainted with each other and achieve consensus [3].
2. Social and Political Matters
Through the communications that Muslims have during Hajj, they find out the social achievements and national advances in other Muslim nations and might decide to follow their path. They also learn about the social problems and deficiencies of others and might find solutions by further cooperation. Moreover, they become aware of the real political situations of other Muslim countries, especially the difficulties that sometimes other countries impose on them. For instance, one of the goals of Hajj is to announce the support of Muslims for Palestinians and those oppressed in the world. This helps Muslims to become more united against common enemies of Islam.
To summarize, Hajj is a time that a Muslim finds him/herself in the accompaniment of millions of others who wear as simple as him/her and who repeat the same words as him/her as they move around Ka’aba. This is where “one” is transformed into the totality of ‘people’, establishing the universality of the Islamic community with the goal of approaching Allah.
- References:
- Imam Ali (AS), Nahj-ul Balaqa, Infallible 192
- M. B. Majlesi, "Bihar al-Anwar", vol. 21, p. 105.
- Shaikh al-Hur al-Aamili, “Wasa’il al-Shi’a”, vol. 11, p. 14
Share This Article
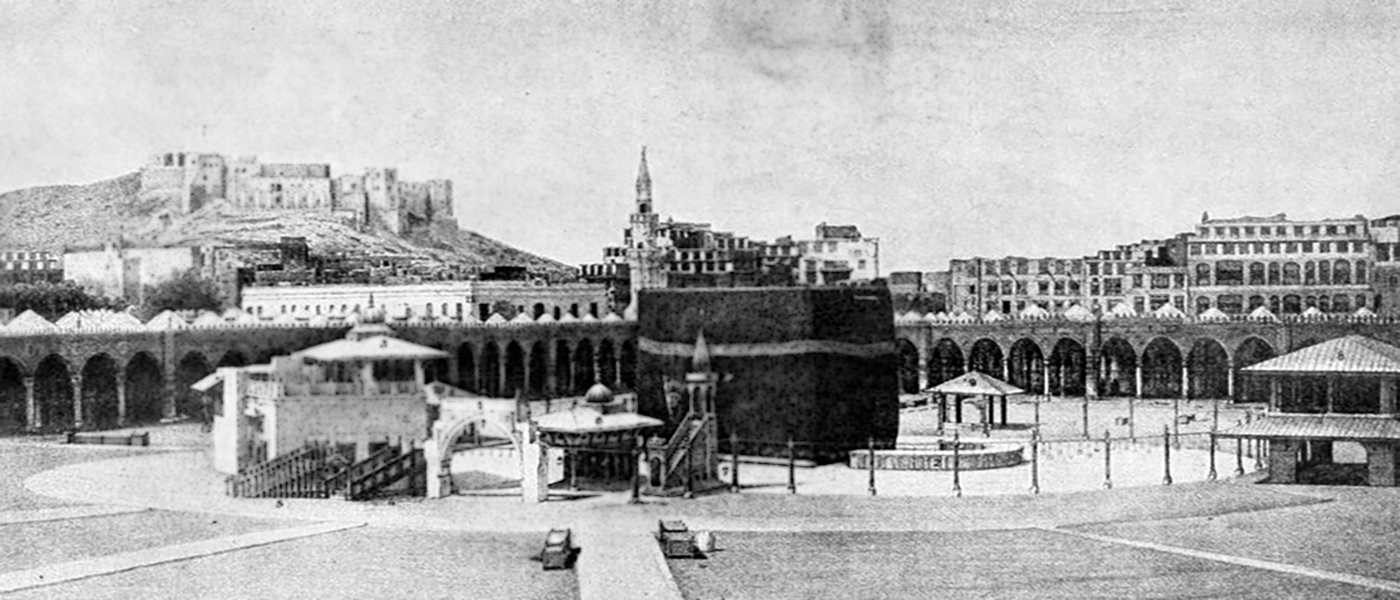
What is the History behind Building the Kaaba?
The word Kaaba means cube in Arabic, and it refers to the square-like building in the holy city of Mecca, which is covered with a silk and cotton veil. It is the most sacred site for Muslims, and millions of people travel to visit that as a pilgrim each year.
Many people think that Kaaba was built at the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) and with the advent of Islam. However, history has a different narration about which we are going to talk in this article.
1. The First People who Built Kaaba
The first person who built Kaaba was Adam (PBUH), and it was remained unharmed until the great flood at the time of Noah (PBUH) [1], which caused it to be partially damaged. Afterward, the structure of the Kaaba was reconstructed by prophet Abraham (PBUH) and his son, Ishmael, under the command of Allah. The Quran has narrated this story in this verse:
As Abraham raised the foundations of the House with Ishmael, [they prayed]: 'Our Lord, accept it from us! Indeed, You are the All-hearing, the All-knowing. (2: 127)
2. Kaaba Between Abraham (PBUH) and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
The son of prophet Abraham (PBUH), Ishmael (PBUH), and a tribe named Jorohom were the guardians of Kaaba after the demise of prophet Abraham (PBUH). This magnificent building stood upright until that Jarhim tribe, and then a tribe named Amaaleh rebuilt the square-shaped holy place [2]. Years after, one of the predecessors of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) named Qusai Bin Kelab, made a wooden structure to protect the building and neighbored it with another building Called Dar-ol Nadvah, which was the governor's state. Then he asked each Quraysh tribe to locate their houses mirroring one side of the Kaaba, to build a circle around it. Some say that Kaaba was once ruined in flood before the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP), but that again is not proven [3].
3. Kaaba and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
When Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was chosen as the Messenger of Allah, Kaaba was considered a holy place. Some reference books say that Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) took part in the reconstruction of the Kaaba after the flood. Also, there was a fight between the Arab clans about where to locate the Black Stone, and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was chosen as the trustee of all clans to locate the holy stone on the eastern side's edge. (4) Kaaba was filled with idols and statues when Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) left Mecca because of the severe tortures and problems the Arab clans made for him and his followers. Even years before, Kaaba was a place to worship the idols.
When Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) gathered his followers and returned to Mecca, he ruined all those idols with the help of his first follower and friend, Imam Ali Ibn Abi Talib (AS). Kaaba became a center of performing Hajj and the Qibla [i] of the Muslims. The Dome of Rocks (Qubbat al-Ṣakhrah ) was the first Qibla of Muslims, but Allah inspired Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) to change it toward the Cubic Kaaba.
4. Kaaba After Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
Kaaba has been reconstructed many times after the demise of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP), but the cubic shape of the building has never been changed. Now, the Saudi Arabian Government is responsible for preserving this sanctuary, though it belongs to all Muslims and all nations. There are many different parts and holy sites around Kaaba, like the Black Stone, the Iraqi corner, the Kiswa, or the black covering, which we are going to discuss in our next articles.
Notes:
[i] Qibla is the direction to which all Muslims say their prayers.
References:
- Arzaghi, Abu Valid Kaaba News and What happened to that, Vol. 1, P 68.
- Seyyed Hashem Bahrani,Tafsir Al-Burhan Vol. 1 P 301 Hadith 36.
- Rasouli Mahallati, Hashim Analytical History of Islam (2), (1991) Tehran, Iran.
- Guillaume, A. (1955). The Life of Muhammad. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 84–87.
Read More

The Philosophy of Hajj Rituals
Hajj literally means ‘heading to a place’. In Islamic terminology, however, it refers to the obligatory annual pilgrimage that Muslims make to Mecca with the intention of performing certain religious rites following the method prescribed by Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) [1].
In essence, Hajj is man's evolution toward Allah. It is social worship that creates a relationship between God and His creatures and has different effects on Islamic society. The performance of Hajj simultaneously signifies many things; it is a show of history, the Islamic doctrine, and that of Islamic unity and brotherhood [2]. Hajj reinforces the religion, i.e., it makes millions of Muslims gather in Ihram; this gathering strengthens the relationship between the followers of Islam and makes their hearts grow closer.
The history of Hajj rituals goes back to the time of Prophet Adam, who was first entrusted by Allah to build the Kaaba, the House of Allah. He and his descendants were the first people to perform Hajj rites. The rites continued up until the time of Prophet Abraham who was ordered by God to rebuild Kaaba along with his son Ishmael:
“When we settled for Abraham the site of the House [saying], Do not ascribe any partners to Me, and purify My House for those who go around it, and those who stand [in it for prayer], and those who bow and prostrate” (22:26).
After building the Kaaba, Prophet Abraham would perform Hajj every year, and this practice was continued by his son after his death. However, gradually with the passage of time, both the form and the goal of the Hajj rites were changed. Kaaba had turned into a place of idolatry, and the people had totally abandoned the teachings of their leader, Prophet Abraham until the time came for his supplication to be answered:
“Our Lord, raise amongst them an apostle from among them, who should recite to them Your signs, and teach them the Book and wisdom, and purify them. Indeed You are the All-mighty, the All-wise” (2:129).
After a long time [i], a man by the name of Muhammad ibn ‘Abdullaah was born in the very city that Prophet Abraham had made this supplication. For twenty-three years, Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) spread the message of monotheism (Tawhid) – the same message that Prophet Abraham and all the other Prophets carried – the most important message of Hajj.
Not only did Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) purify the Kaaba from idols and all the defilements, but he also reinstated all the rites of Hajj and banned all indecent and shameful acts. Consequently, Kaaba became the universal center for the Muslim worshippers of the only true God, once again [3].
Hajj Rituals
Annually, Muslims from all over the world are encouraged to participate in this great "pilgrimage" (Hajj). Everyone is considered equal. There is no discrimination on the basis of people’s race, sex, or social status.
There are secrets about Hajj exoteric rituals that are somehow beyond man’s understanding and so not easy for everyone to learn. Some steps of the Hajj rites are reminiscent of the events associated with Abraham, Ishmael, and his mother Hagar, and personify their self-sacrifice, altruism and struggle with Satan in the path of Allah [4]. This would help us understand the philosophy behind some of the acts performed in Hajj.
Ihram
The performance of Hajj begins at Miqat, a place where pilgrims should wear Ihram and from there go for Hajj or Umrah. Donning such unsewn white garments entirely distances man from material ostentations and engrosses him in a world of purity and spirituality. Clothes show individuality and distinction.
They create superficial barriers that separate man from man. The garments of Ihram, however, are the antithesis of that individualism. You join a mass and become nothing but a drop of water in an ocean that has no special identity of its own. Ihram clothing is also a reminder of shrouds that every human has to wear after death. This helps you assume your original shape as a man, just one of the “descendants of Adam” who will die one day.
Hajj is a movement that reminds us of our journey to Allah; “toward Allah is the destination” (24:42). In the state of Muhrim, There is no sex, no perfume, no shoes, no sewn clothes and headcovers for men, no face mask, no cutting of hair or nails, i.e., absolutely no signs of aristocracy or distinction; you don’t even look in a mirror to see your own image.
You don’t hunt any animal; you don’t uproot any plant. So you kill the tendencies of aggression by being peaceful to nature, and this continues until you perform all the rituals and come out of Ihram. All your selfish egos must be buried at Miqat. You witness your own body just like what it looks after death when it is being buried. By sacrificing your individuality, you focus on reality, the basic purpose for which you have been created – that is devoting yourself totally to Allah.
Circumambulation (Tawaf)
Positioned in the center, Kaaba is like a sun while the people are like stars traveling in their orbit of the solar system. Kaaba symbolizes the constancy and eternity of Allah. The moving circle of people represents the continuous activity and transition of His creatures.
This rite is actually the manifestation of Tawhid, the Oneness of God. The heart and soul of the pilgrim should move around Kaaba, the symbol of the House of Allah, in a way that no worldly attraction distracts him from this path. Only Tawhid should attract him. Tawaf also represents Muslims’ unity. During Tawaf, everyone encircles Kaaba collectively.
There is no individual identification of men or women, black or white, red or yellow. The movement has transformed one ‘person’ into the totality of ‘people’ establishing the universality of the Islamic community with the goal of approaching Allah. Likewise, you must reject self-centeredness and step in the way of Allah, which is the way of people. In other words, to approach Allah, you must first genuinely become involved in people’s problems. This is how you are with the people and where you may approach Allah [5].
Maqam
After Tawaf, you have to perform two rak’at of prayer behind Maqam-e Ibrahim [ii] (Abraham's place of standing), which is a very blessed place for praying [6]. It is the nearest point to Allah. As a matter of fact, there is nowhere on earth where you get more rewards than this place for praying. The stone has the footprint of Abraham. He stood over this stone to lay the cornerstone (Hajar al-Aswad), to reconstruct Kaaba, and to pray [7]. By standing on the same stone, you vow to become like Abraham, the upright friend of Allah, who was uncompromising in his conviction of Tawhid [8].
Sa’y
Sa’y literally means to strive, to make an effort to reach an aim. Running between the mountains – Safa and Marwa – seven times, you act like Hagar, the mother of infant Ishmael. After Abraham left her and their son, near the valley of Mecca, Hagar had no food, no water, no shelter, neither for herself nor her child, but only uncompromising, relentless faith that the God of Abraham will not leave her and her son without sustenance.
She started looking out for water, running to the top of the mountains, Safa and Marwa. But she did not find any water. She searched again and again. After running seven times between these two mountains, she came down from Marwa to check on her infant son when she heard the sound of gushing water coming from the sand he had dug under his heels. It was Zam-Zam, a sweet and life-giving fountain of water which was a gift from Allah to the mother and son, and all those who came later. So Sa’y is physical work. It is a struggle to satisfy your needs, and a way to achieve a better life.
The Stay in Arafat Plain
The name Arafat means acquaintance or cognition. There are a few beliefs for why this place has been given this name; in one of the most famous of which, it is held that Prophet Adam and his wife Eve met each other at this plain after they were separated for many years.
It was the devil (Iblis) who misled our forefather -Adam- by telling him to eat from the tree of eternity and possession and caused them to descend from Paradise [9]. They met in Arafat once again, where they became acquainted with one another and with their sins. They made supplications to God and sought His forgiveness. It was in the center of this plain where they were forgiven by Allah. In short, Arafat represents the beginning of man’s creation, that of our forefather Adam. Here you act like Adam or Eve and seek forgiveness for yourself and your loved ones [10].
The Stay at Mash’aril-Haram
Pilgrims of Hajj, returning from Arafat, spend the night between the 9th and 10th of Dhu al-Hijjah at Muzdalifah in the open air. It is here they gather pebbles to hurl at the pillars of Mina (Jamarat). The shortstop at Mash’ar may remind you of your short life on this earth! That you are only a moment of this eternal time. It is for you to think, to plan, to strengthen your spirit, to prepare yourself for the battlefield to fight with the devil. The verse below best describes the philosophy behind the stop at Mash’ar:
“Then when you stream out of Arafat remember Allah at the Holy Mash’ar, and remember Him as He has guided you, and earlier you were indeed among the astray” (2: 198).
Stoning the Pillars (Rami al-Jamrat)
At Mina, the longest and last pause occurs. Millions of freedom-fighters who refuse to obey any power except Allah crowd here.
It has been said that Satan appeared in front of Prophet Abraham at this place three times when he wanted to sacrifice his son under God’s command. Satan tried everything to put doubt in his mind, but Prophet threw seven pebbles at him each time and made him run away. The Devil also tried to pervert the mother and the son to prevent Abraham from obeying God’s command, but they stayed firm in their resolution.
This deed became so monumental that it was made a rite of Hajj to teach us that Satan tries to misguide one sometimes through the spouse or offspring and sometimes approaches directly. Only strong faith in Allah can save us from this evil influence.
Sacrificing an Animal (Qurbani)
During Hajj you are to:
Declare monotheism by Tawaf.
Exercise the struggle of Hagar by Sa’y.
Show the descent of Adam by going to Arafat from the Kaaba.
Show the philosophy of man's creation, the evolution of thoughts from pure science to pure love, and the ascension of the spirit from mud to God by going from Arafat to Mina.
The last stage of evolution and absolute freedom from earthly desires with full submission to Allah is here, in Mina. It was at this plain that both the father and the son - Abraham and Ishmael - had surrendered to Allah, where Abraham was being tested to see whether he was capable of overcoming his personal feeling of love for his son for the sake of Allah, to check whether he was prepared to sacrifice his son. But when he was ready, his Ishmael was returned unto him unharmed:
“O Abraham! You have indeed fulfilled the vision” (37:104).
The lesson that would be learned here is if you love something more than you love Allah, then that thing has become your idol, and you must be ready to sacrifice that. You must be prepared to slaughter your worldly desires, worldly love, your Ishmael in Mina in order to be free from all worldly attachments. If you are, then slaughter a goat, sheep, ram, cow, or camel instead: “Thus do We reward the virtuous” (37:110).
“It is not their flesh or their blood that reaches Allah. Rather it is your God wariness that reaches Him. Thus has He disposed of them for your benefit so that you may magnify Allah for His guiding you. And give good news to the virtuous” (22:37).
Cutting Hair (Taqsir)
After sacrificing an animal, you are to spurn your earthly pleasures once again by shaving or trimming your hair [iii]. You become free from whatever that stands between you and God even if it is as small as superficial beauties.
You acknowledge the Divine beauty by putting aside your pride and arrogance, and cleanse your soul and spirit from impurities. Consequently, it is by this sheer servitude to Allah that you reach absolute freedom.
When you first approached Kaaba, you had not, by then, purified yourself. You were still impure and unconscious. In Arafat, you gained consciousness. In Mina, you purified yourself. So, this is appropriate that you do the Tawaf and Sa’y in the purified state once again before you complete your Hajj and totally come out of Ihram.
Circumambulation of Women (Tawaf-Un-Nisa)
It is obligatory for both men and women -either married or single- to perform Circumambulation of women (Tawaf-Un-Nisa). This shows the importance that Islam place on blissful married life and its effects on the family institution and the whole society.
Allah has made the husband promise to treat his wife well:
“Treat them (wives) kindly” (4:19).
As soon as the Ihram clothing for Hajj is donned, the husband and wife become prohibited for each other till the end of the rituals. As a matter of fact, marriage (Nikah) bounds a man and a woman into a married couple; in the same way circumambulation of women (Tawaf-Un-Nisa) and its prayer again reinstate the relationship of the couple. The mistakes they have made in the past get pardoned, and they are given a chance to start a new relationship, to be very careful in performing all their duties in their married life and family unit.
This is the latter Tawaf of the Kaaba, performed after you return from Mina. In Mina, you have defeated Satan and renewed your ties with Allah by following the footsteps of Abraham before you return home. During the rituals of Hajj, you played the roles of Abraham and Hagar. Do not replace your role-playing to something else when you return. Like Hagar, always trust in Allah. Like Abraham's fight against oppression. Like Abraham be prepared to sacrifice your Ishmael, i.e., love or desires, for the sake of your faith. That is the essence of Hajj. You return to Allah the way He wanted you to be: a slave totally dedicated to his/her Lord.
Conclusion
During Hajj rituals, and before Muslims return home, they defeat Satan and renew their relationship with God. They learn always to have faith in Allah and to be prepared to sacrifice their desires for the sake of Him. The rites of Hajj remind us of the Islamic axioms, i.e., monotheism (Tawhid), prophethood (Nubuwwah) and the afterlife (Ma’ad).
They also indicate the importance of unity in the Islamic community. Ultimately, Muslims return home with a reserve of knowledge and experience to share with their society. If accepted by Allah, this holy experience could remain like a glittering beam in their whole life.
The Holy Prophet said: "The daily prayer, Hajj, circumambulation, and other rites are aimed at remembering Allah. But when there is no remembrance of Him in your heart, what value will your oral remembrance have?"
Accordingly, faith is based on three important stages; acknowledgment by heart, affirmation by words, and performance of the principles.
Notes:
[i]. According to some historical texts, after about more than three thousand years.
[ii]. A large stone on which Prophet Abraham stood while building the upper walls of Kaaba. It is believed that this rock was sent to Abraham from heaven along with three other rocks, the other one of which is the sacred black stone (Hajar al-Aswad).
[iii]. Women should not shave their heads; they only trim slightly at the end of the lock of hair. However Shaving the head is obligatory for men if it is the first time they are performing Hajj.
References:
- History of Hajj
- Hajj
- History of Hajj
- Circumambulating
- (2:125)
- (2:125)
- the soul of Hajj
- (20: 120,121,122,123)
- Hajj
- (22:29)
Read More

