

What is the Philosophy of Prayer in Islam? Part 2
Prayer in Islam (Salat) is one of the most important practical principles of Islam [1]. It is a physical, mental and spiritual act of worship consisting of prescribed actions and words. Every action in the prayer in Islam (Salat) is meaningful and if you want to know the Philosophy of Prayer in Islam, we will see what each movement in the prayer means and represents.
The Philosophy of Prayer in Islam
Standing (Qiyam)
The prayer in Islam starts with standing. That is to appear in front of God gently and courtly with your whole heart and body; that is how one demonstrates the respect for others. Having the gaze down in Qiyam demonstrates the modesty towards God. It makes one forget about his\her superiority and helps to overcome his\her arrogance [2]. Also, knowing that one should stand five times a day in front of a superior power, who knows every overt and covert act and behavior, will eventually prevent from evil deeds and sins [2].
Intention (Niyyah) of the Prayer in Islam
We do many things every day, some of which are repetitive and by habit, and we are not even aware of why we are doing them. Prayer in Islam, one of those works, seems to be a physical practice. That is why the prayer must have a Niyyah to prevent the prayer from becoming a daily habit and to help the Muslim to recall the reason behind that. Hence, a prayer without Niyyah will be a set of physical movements, and it won’t be accepted.
Niyyah reminds one that he\she is showing up to demonstrate the submission to the divine orders. Having a pure intention in the prayer teaches to avoid duplicity. It is not necessary to repeat the words of the Niyyah. That is enough to recall it and to consider it throughout the prayer. Indeed, this should be considered during any other act or practice in daily life; firstly, to purify our intentions for God; then, to stick to that intention until the end.
Takbir
The sayings in the prayer in Islam (Salat) start with Takbir. Takbir means to regard God as great. By saying Takbir, we express our belief that God is great. There exists nothing similar to Him. He cannot be perceived or touched by our physical senses and understanding [3]. Takbir reminds us of the Monotheism (Tawhid) which is the first pillar of Islam [4].
Bowing (Ruku)
Bowing (Ruku) is a perfect demonstration of the gratitude and respect that a human being has for God, as a divine source and a higher power. And, this is a unique posture that a Muslim will never have in front of anyone else [5]. In Ruku, every individual, in whatever position and grade, bows to God which consequently reduces the arrogance and pride within him\her. Lady Fatima (AS) said: “God has ordered […] the prayer to purify you from arrogance and pride” [6].
According to Imam Ali (AS), holding the neck straight during Ruku shows that one believes firmly in Islam such that he\she won’t give up even if he loses his\her life (to have the neck cut) for this belief. Another point in Ruku is that it is a unique posture that only exists in the Islamic ritual and distinguishes the Islamic prayer.
Prostration (Sujood)
Prostration (Sujood) is exhibiting the maximum humility and dignity for God. Imam Sadiq (AS) describes that one is closest than ever to God in this posture [7]. According to the Quran: “to Allah prostrates whatever is in the heavens and whatever is on the earth of creatures…” (16:49). This means that in that posture, the human being is in harmony with the whole universe and creatures.
Imam Ali (AS) explained that the first Sujood means that God has created us from the earth. Coming up from the first Sujood is the symbol of this worldly life. The second Sujood represents the death and returning to the earth. Finally, rising from the second Sujood symbolizes the afterlife [8]. According to the interpreters of the Quran, this refers to the fact that: “From the earth, We created you, and into it, We will return you, and from it, We will extract you another time” (20:55).
The Prayer in Islam, Beneficial to Soul as Well as Body
There have been some attempts in the recent years to analyze and justify the physical benefits of performing the prayer. Those discussions might be true, but they are not the whole reason behind this practical principle of Islam. The prayer is a means of worship that engages the body and soul and is beneficial to both. The reasons above are a small part of the philosophy behind the acts of the prayer. One might refer to the advanced references for more details.
References:
- Shaikh al-Hur al-Aamili, "Wasail al-Shia", p. 214.
- J. Maleki Tabrizi, “The Mysteries of the Prayer”, vol. 1, p. 323.
- Ibn Babawayh, "Man la yahduruhu al-Faqih", Book Salat, Chap. 17
- Monotheism Tawhid
- A. Hosseini Khamenei, “The Prayer in Depth”, p. 5.
- M. Majlisi, "Bihar al-Anwar", vol. 29, p. 223.
- Shaykh al-Kulayni, "al-Kafi", vol. 3, p. 324, T. 11.
- Ibn Babawayh, "Man la yahduruhu al-Faqih", vol. 1, p. 311.
Share This Article
Is Islam Compatible with Feminism?
Feminism is a movement of the modern times and may not have been heard at the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH). Issues like feminism that belong to the new era should be considered from different aspects to see if they are compatible with Islam or not. In most of the similar issues, Islam has some common views and some contradictions.
To find out if Islam accepts feminist theories and ideas, and advocates of feminism, we should first understand what feminism is and when and why it arose?
The Main Purposes of Feminists
The first feminist movement started, to gain some rights for women. These include “guardianship of infants, property rights, divorce, access to higher education and the medical professions, equal pay and protective legislation for women workers - many of which women are still campaigning for today!” [1]
As I mentioned, these issues are not restricted either to western countries or countries with a majority of Muslim population. Even in Muslim countries, there were unfair social and family treatments toward women. We will later discuss the fact that it is not the Islamic rulings that subordinate women, but the traditions of those countries who embraced Islam within years.
Thus feminism, which started in 1848 in America, gradually spread over the world. Women and some men who were in favor of women’s rights became feminists without having a real knowledge of feminism [2].
What is Common in Islam and Feminism?
Although I mentioned that in Muslim countries, women were not treated fairly and some of them became feminist, it never means that the unfair treatments toward women were because of Islamic rules. The fact is that the unjust treatment of women is sometimes due to different cultures and traditions. This unjust treatment existed at the time of pagans even before the birth of Islam.
It was a common act between pagans of Arab peninsula who used to be ashamed of their girls and prefer boys over girls. They used to bury their infant daughters alive, as they used to consider them inferior to men.
Quran describes the attitude of pagans toward their baby girls clearly; “When one of them is brought the news of a female [newborn], his face becomes darkened, and he chokes with suppressed agony. He hides from the people out of distress at the news he has been brought: shall he retain it in humiliation, or bury it in the ground! Behold! Evil is the judgment that they make.” (16: 58 -59)
In these conditions, where women were inferior to men, Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) came with the Quran which gave women a high position and value.
It is narrated in history that Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) had a few sons who all died at a young age. Then he was granted a Daughter. Pagans used to humiliate him for not having a son to keep his family lineage. Then this chapter was revealed to him:
“Indeed We have given you abundance. So pray to your Lord, and sacrifice [the sacrificial camel]. Indeed it is your enemy who is without posterity.” (108: 1-3)
And from his only daughter, his generation continued until now which is an honor for a large group of Muslims.
The Status of Women in Islam
Most of the rights that feminists are campaigning for in this era were mentioned in the Quran 1400 years ago;
Property Rights
“To men belongs a share of what they have earned, and to women a share of what they have earned.” (4:32)
According to Islam, women have a complete right to have an earning. They also have the right to use their earnings in any way that they desire. Besides, men have the obligatory responsibility to pay for women’s daily expenses;
“Men are the managers of women, because of the advantage Allah has granted some of them over others, and by virtue of their spending out of their wealth.” (4: 34)
The Right to Work in Key Positions
At the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH), there were many women who used to work in the market to earn money for their living. Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) not only encouraged them for their job but also taught them the right Islamic rules of business and commerce. The most significant example was Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) himself who used to trade for Lady Khadijah (AS).
Access to Higher Education
According to Islam, gaining knowledge is obligatory for both men and women and knows no time limit in one’s life. Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) says: “Gaining knowledge is an obligation upon all Muslim men and women.” [3]
Marriage and Divorce
Women have the right to choose their husbands. They have the right to ask the court for separation as well if for any logical, reasonable purpose they do not wish to continue their married life.
Spiritual Equality
“Whoever acts righteously, [whether] male or female, should he be faithful, We shall revive him with a good life and pay them their reward by the best of what they used to do.” (16:97)
All the above points and what will follow in this article is emphasizing on the point that according to Islam, men and women do not have the same rights, but their rights are equal.
Why Equal Rights and not Same Rights?
Murtaza Mutahhari argues that for having equal rights in the society, is it necessary to have the same rights too? He gives an example of a father who would like to divide his wealth between his children. He has a farm, a piece of land and a business company, the price of them, moneywise, is the same but they do not look the same.
The father knows his children, their talents, and interests. So, he gives each of his properties to each child based on his knowledge of the child’s potential. In this example, while the price of the properties is the same, but they are not equal for all children. [4]
The same is with the rights of men and women. They have equal rights according to their talents, potential, and biological features, but their rights are not the same.
Efforts to Reconcile Islam with Feminism
Although Islamic treatment of women is fair and for the benefit of women, family, and society, still there are feminist campaigns that try to show Islamic rules are against women’s rights. Some of the Islamic rules that are usually mentioned by feminists are as follows:
The Islamic Dress Code
It is acceptable that wearing the Islamic dress code may cause some hardship for Muslim women, but nothing can be reachable without accepting its difficulty. Just like a mother who can never enjoy the sweetness of having a baby, unless she goes through nine months of pregnancy.
Thus, wearing the Islamic dress code that will lead to better family life and a safer society is worth its difficulty. Same is with the right to have free relationships with the opposite sex, which is forbidden according to Islam without specific conditions. This applies to both men and women to strengthen the base of family.
Men Having Authority over Women
The authority that Islam gives to men over their wives is the authority of family management. It does not mean that they can be oppressive towards women.
Polygamy
Polygamy is also an Islamic rule that can take place under certain conditions. But it does not give the right to all Muslim men to marry more than one wife. So, neither men should misuse this Islamic rule for their own benefit, nor it should be taken as a tool of undermining Islam without enough knowledge about the issue [i].
Inheritance
According to Islam men have a twice a share of a woman in inheritance: “for the male shall be the like of the share of two females.” (4:11)
Imam al-Sadiq (as) was asked for the reason of this ruling in Islam, and he replied “that it was because Islam had exempted woman from armed combat, and moreover that dower and maintenance had been imposed upon man for her benefit. What is more, in certain cases of doubt, in which blood relatives had to pay ransom money, a woman has been exempted from sharing with others in the payment.
These are the causes why the share of a woman is less than the share of a man.” Thus, it is “the special situation of woman in inheritance is the effect of dower and maintenance is the effect of dower and maintenance and exemption from armed combat and paying ransom money.” [5]
Are Men and Women Equal according to Islam?
According to Islam men and women do not have the same rights, but they have equal rights, which differ from each other according to each person’s biological, physical, and spiritual differences. An example is that Muslim women are not allowed to become judges, which is because of their high level of emotions which is required for a wife and a mother.
The love that a wife and a mother provide for the family is what makes the base of a family firm. While men are more logical to support the family by reason and making tough decisions at critical points. So, it has become an obligation on men to supply for the family or go for defense in war situations. There is no obligation over women in these cases.
This does not mean that women cannot put enough effort to strengthen their reason for their emotion. But if they do so, they have changed their nature, and their life path will be totally changed, in a way that they may never reach the safety and comfort that a woman requires.
Conclusion
If Muslims act according to the Islamic rules and commands, they will not need any of these feminist ideas. Since many of those rights that feminists are trying to gain are already given to Muslim women according to Islamic law.
It is good to keep in mind that the ultimate goal of every human in this life is to reach safety and calmness. This is easier and faster to gain by obeying the rules of Islam, simply because these rules have been ordained by the creator of human beings.
Thus, we can conclude that Islam is not completely compatible with feminism. Islam accepts those points of feminism that is for the best of human beings and the society. And will reject the rights that feminism defines for women while they would harm the woman, family and the society.
Notes:
[i] Find information about Islamic rules on polygamy here: https://www.salamislam.com/content/why-does-islam-allow-polygamy-part-1/3
References:
- Feminism
- ibid
- Amali Al-Sadouq, p. 419.
- Mutahhari, Murtaza, The rights of Women in Islam, p. 115
- Mutahhari, Murtaza, The rights of Women in Islam, p. 225
Read More
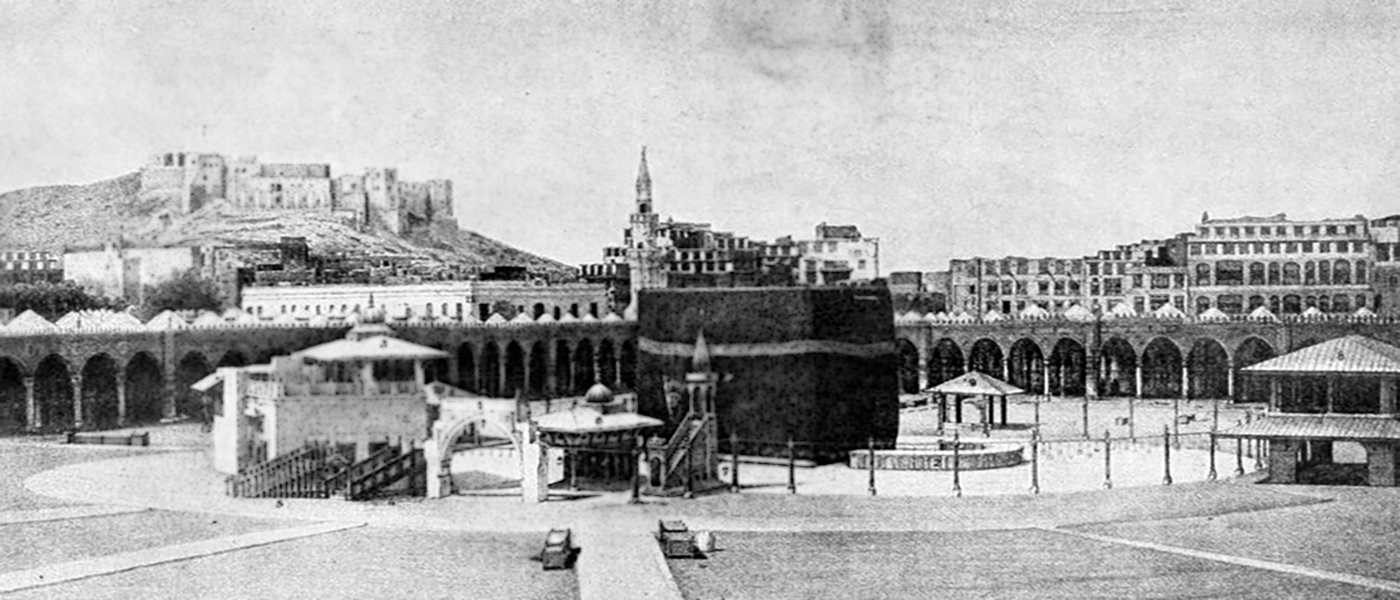
What is the History behind Building the Kaaba?
The word Kaaba means cube in Arabic, and it refers to the square-like building in the holy city of Mecca, which is covered with a silk and cotton veil. It is the most sacred site for Muslims, and millions of people travel to visit that as a pilgrim each year.
Many people think that Kaaba was built at the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) and with the advent of Islam. However, history has a different narration about which we are going to talk in this article.
1. The First People who Built Kaaba
The first person who built Kaaba was Adam (PBUH), and it was remained unharmed until the great flood at the time of Noah (PBUH) [1], which caused it to be partially damaged. Afterward, the structure of the Kaaba was reconstructed by prophet Abraham (PBUH) and his son, Ishmael, under the command of Allah. The Quran has narrated this story in this verse:
As Abraham raised the foundations of the House with Ishmael, [they prayed]: 'Our Lord, accept it from us! Indeed, You are the All-hearing, the All-knowing. (2: 127)
2. Kaaba Between Abraham (PBUH) and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
The son of prophet Abraham (PBUH), Ishmael (PBUH), and a tribe named Jorohom were the guardians of Kaaba after the demise of prophet Abraham (PBUH). This magnificent building stood upright until that Jarhim tribe, and then a tribe named Amaaleh rebuilt the square-shaped holy place [2]. Years after, one of the predecessors of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) named Qusai Bin Kelab, made a wooden structure to protect the building and neighbored it with another building Called Dar-ol Nadvah, which was the governor's state. Then he asked each Quraysh tribe to locate their houses mirroring one side of the Kaaba, to build a circle around it. Some say that Kaaba was once ruined in flood before the time of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP), but that again is not proven [3].
3. Kaaba and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
When Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was chosen as the Messenger of Allah, Kaaba was considered a holy place. Some reference books say that Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) took part in the reconstruction of the Kaaba after the flood. Also, there was a fight between the Arab clans about where to locate the Black Stone, and Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) was chosen as the trustee of all clans to locate the holy stone on the eastern side's edge. (4) Kaaba was filled with idols and statues when Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) left Mecca because of the severe tortures and problems the Arab clans made for him and his followers. Even years before, Kaaba was a place to worship the idols.
When Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) gathered his followers and returned to Mecca, he ruined all those idols with the help of his first follower and friend, Imam Ali Ibn Abi Talib (AS). Kaaba became a center of performing Hajj and the Qibla [i] of the Muslims. The Dome of Rocks (Qubbat al-Ṣakhrah ) was the first Qibla of Muslims, but Allah inspired Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP) to change it toward the Cubic Kaaba.
4. Kaaba After Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP)
Kaaba has been reconstructed many times after the demise of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH&HP), but the cubic shape of the building has never been changed. Now, the Saudi Arabian Government is responsible for preserving this sanctuary, though it belongs to all Muslims and all nations. There are many different parts and holy sites around Kaaba, like the Black Stone, the Iraqi corner, the Kiswa, or the black covering, which we are going to discuss in our next articles.
Notes:
[i] Qibla is the direction to which all Muslims say their prayers.
References:
- Arzaghi, Abu Valid Kaaba News and What happened to that, Vol. 1, P 68.
- Seyyed Hashem Bahrani,Tafsir Al-Burhan Vol. 1 P 301 Hadith 36.
- Rasouli Mahallati, Hashim Analytical History of Islam (2), (1991) Tehran, Iran.
- Guillaume, A. (1955). The Life of Muhammad. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 84–87.
Read More

